Student engineers design, build, test lunar rovers

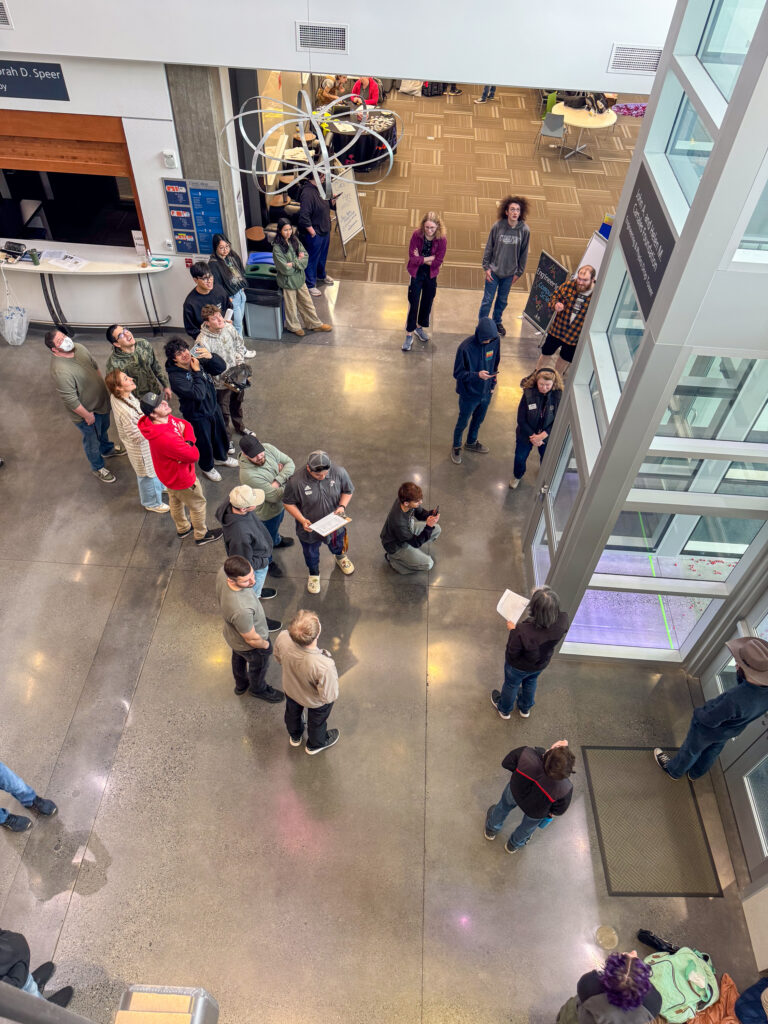
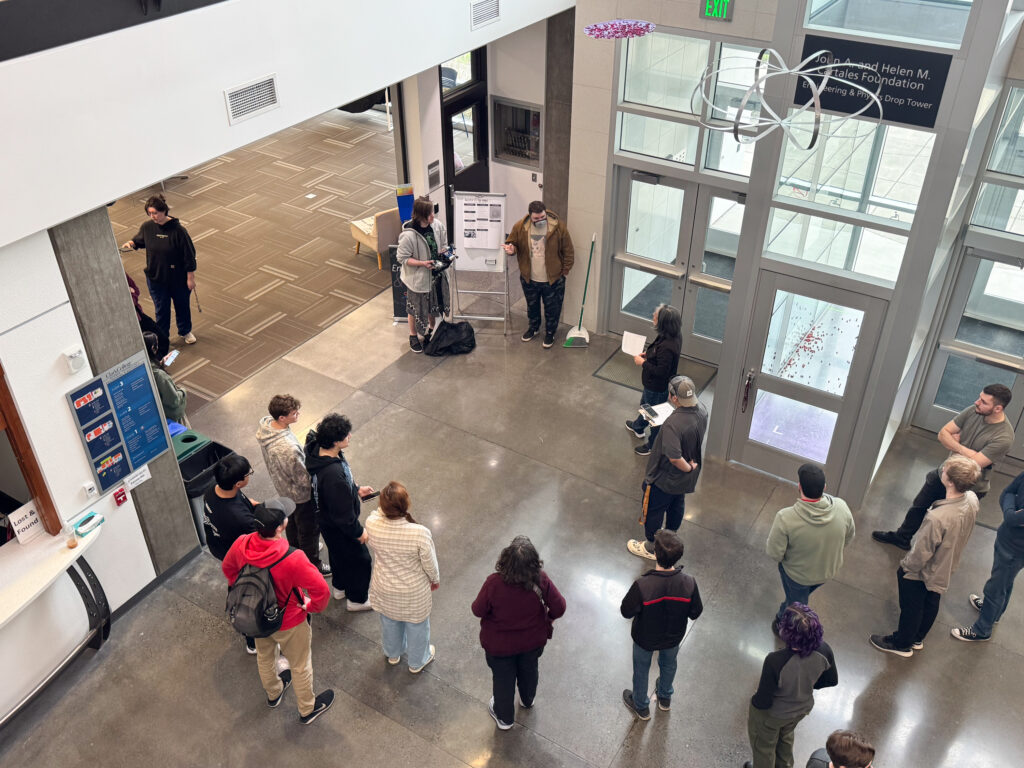
The anticipation was sky-high in the Clark College STEM Building on March 11. Engineering students gathered near the drop tower in the three-story foyer and waited.
“Doors closing,” announced a student with a clipboard. The countdown began: “5, 4, 3, 2, 1!”
All eyes turned upward.
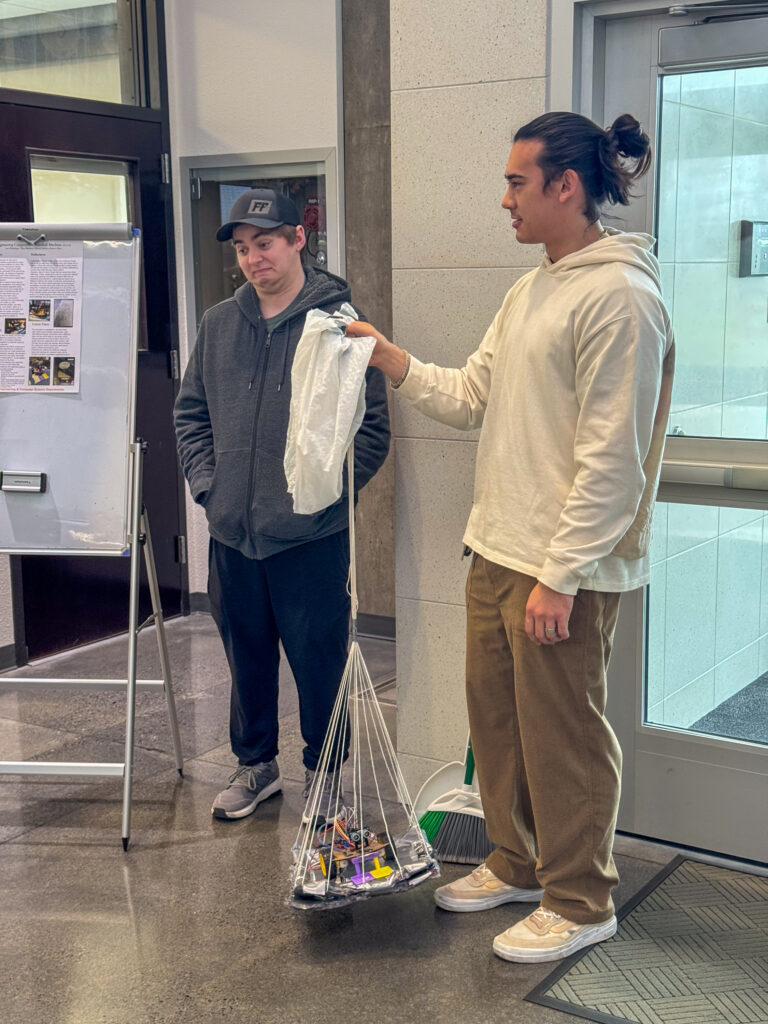
Then—whoosh! A robotic lunar rover plummeted from three stories above. Gasps filled the air as its parachute deployed, sending the rover gliding gently toward the ground.
Now for the real test: Would it land in one piece? Could it navigate the terrain, scoop up moon rocks (a.k.a. plastic balls), and cross the finish line—all on its own power?
Every term, engineering professors Tina Barsotti and Carol Hsu pose a real-world problem to their students and instruct them to design and build an object that solves the problem. Teams of students work together. At the end of each term, teams present their prototype to their peers, explaining their process and materials used. Finally, teams test their designs.
The Project Artemis Challenge
Engineering students were given this challenge during winter term:
Design an autonomous device that can withstand a three-story drop, collect as many gumballs as possible, and move to a designated end zone within the time limit.
Designed with NASA’s Project Artemis in mind, the purpose of this device is to collect geological samples from the moon’s surface.
To simulate landing on the moon, student engineers dropped their rovers from the STEM Building’s three-story drop tower. Most teams designed a parachute to slow the fall. If the vehicle survived the drop, its mission was to pick up as many gumballs as possible (simulating moon rocks) and cross the finish line—without human intervention.
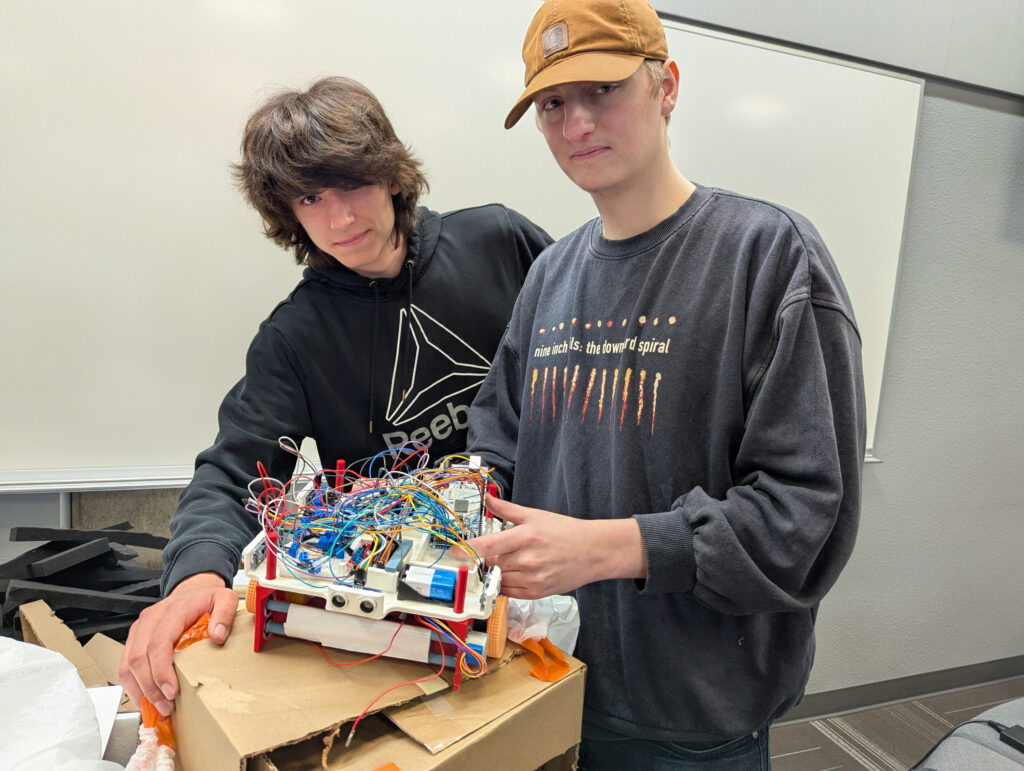

Professor Carol Hsu said, “This project is particularly challenging as it requires withstanding a drop before completing a task. However, students consistently rise to the challenge and gain invaluable experience.” She added, “One of my students shared, ‘My daughter became interested in learning more about robotics after watching the competition!’”
During the winter engineering challenge, some teams’ projects succeeded and made it across the finishing line with “lunar rocks.” But a larger number didn’t survive the three-story drop. One of those teams, Isaac Newton’s Dog Diamond, gathered the pieces of their broken lunar rover and carried them back to a table to assess the damage.
One group reported: “We learned that the trial-and-error process does, in fact, involve error. These experiences taught us the importance of adaptability and persistence in problem-solving. If we were to do this project again, we’d spend more time on testing and making prototypes to improve the design.”





Designing within Engineering Parameters
Each team was required to design and build their vehicle to adhere to strict parameters.
Design specifications:
- Size: Must fit within a 35 cm x 35 cm x 35 cm box
- Weight: Must weigh less than 2.0 kg
- Power source: Must be self-contained in the device
- Mobility: Must be fully autonomous
- Design: Must be students’ own design, outside of motor components
- Cost: Must cost less than $100
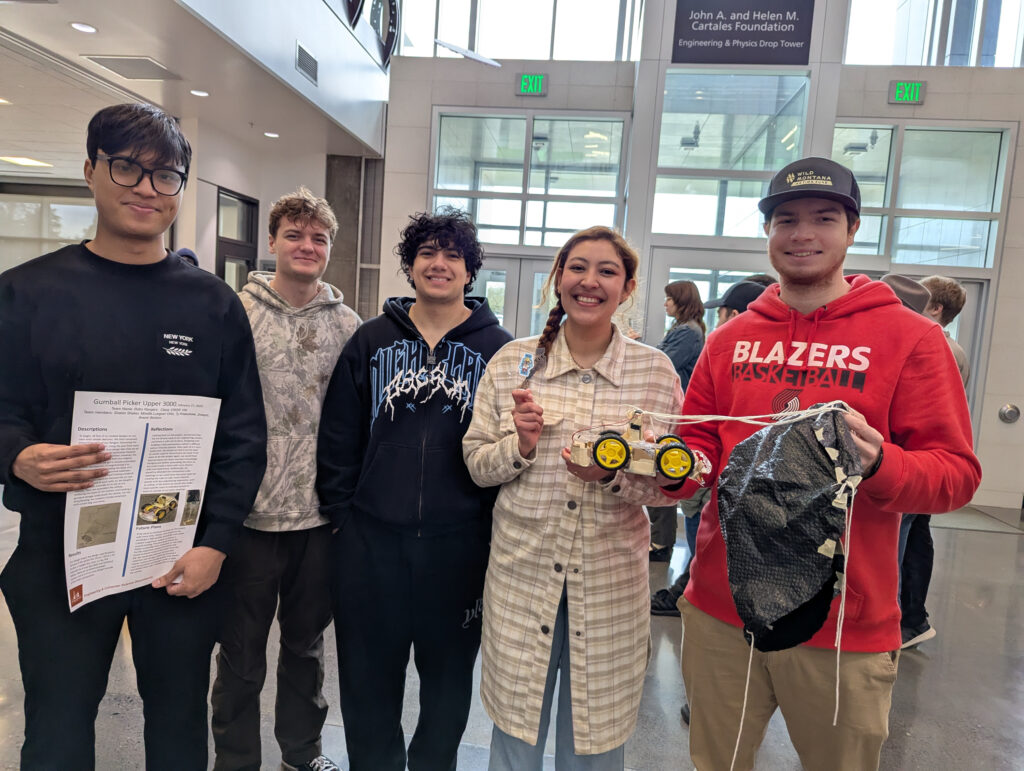
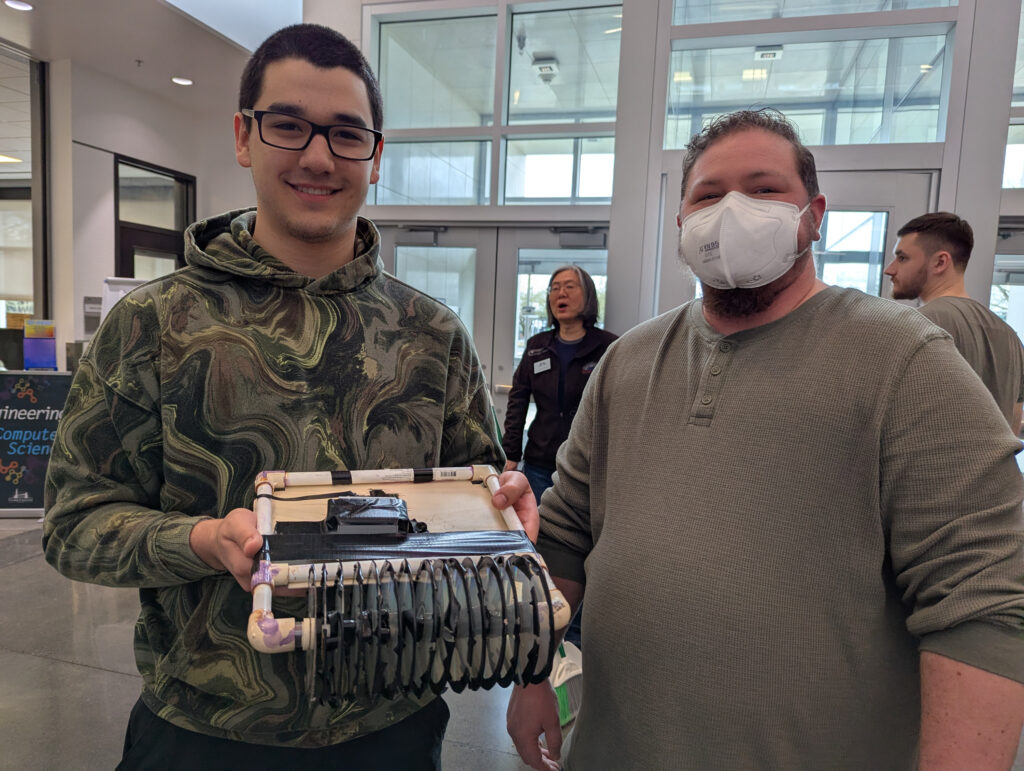
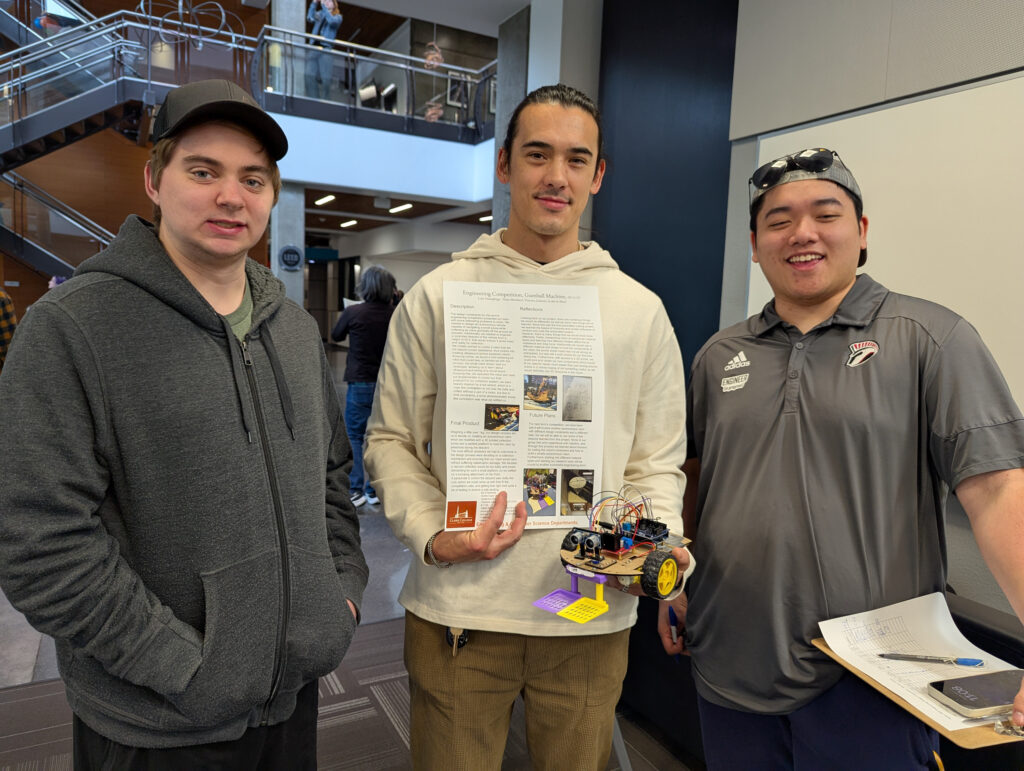
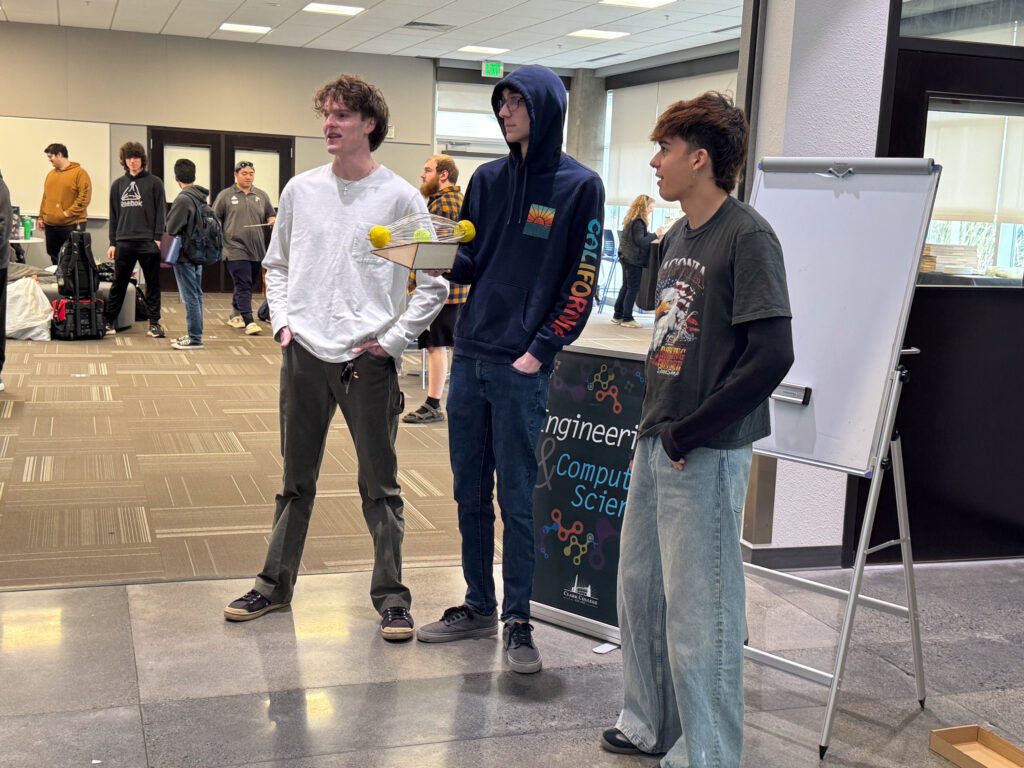
Materials: Student engineers used a variety of materials including 3D printed filament, balsa wood, CDs, modeling clay, threaded metal rods, and various kinds of wheels and axles. Designs also incorporated electronics or a motor and power box within the body of the robot, and a parachute to reduce the descent speed.
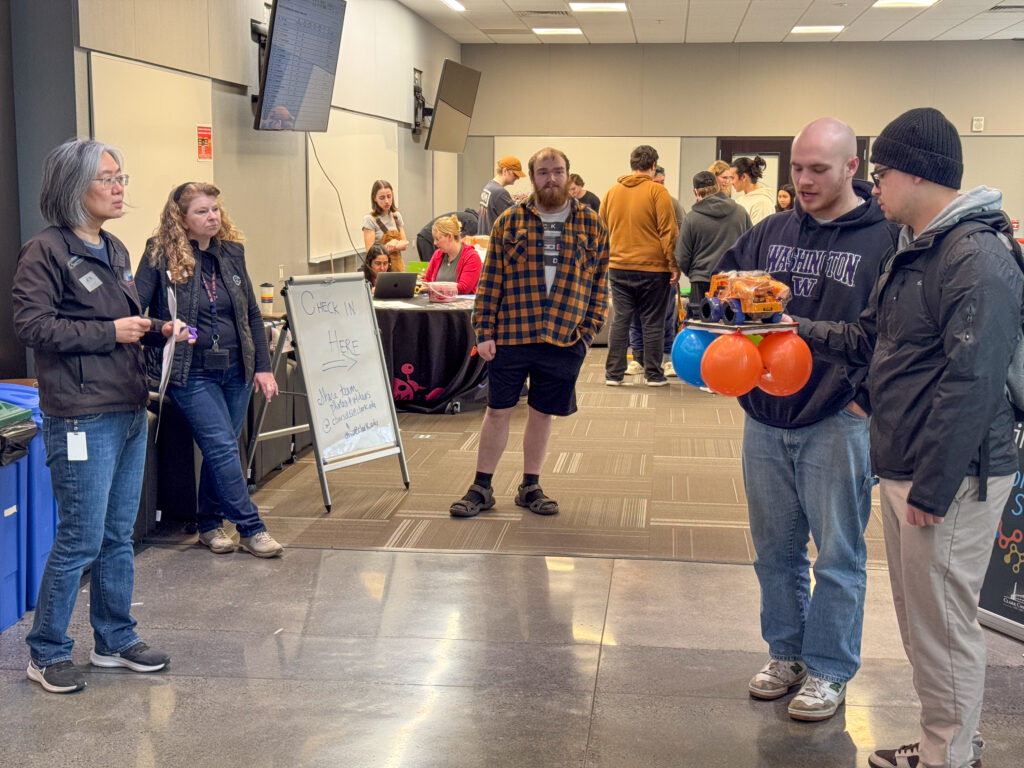
Teams: Engineering students comprised 18 teams including The Argonauts, Imperfectly Designed, Robo Legs, Robo Rangers, Sisters in Science, Innovation Nation, Safety Hazards, Blue Moon, and Isaac Newton’s Dog Diamond.

Throughout the morning, all 18 teams presented their designs and then climbed the stairs to test their projects in the drop tower. After testing their autonomous vehicle, students examined what worked, what didn’t, and how they would improve it.
One group reflected: “Looking back on this project, we learned that we are all very early in our engineering careers and there is still a lot to learn. Designing and building a fully autonomous vehicle is difficult and an intricate process. Also, Open AI is a very useful tool…that can be used to create code for the purpose we need. If we were to do this project over again, we would have learned about our team members’ knowledge and backgrounds before assembling the team so we could create a team with more diverse skills and experience.”
Another group reported: “We utilized our engineering knowledge and available tools to optimize our machine’s efficiency. As we deepen our understanding of engineering coding, we recognize that programming could significantly improve our design.”

Early Pi Day Celebration
After all the tests were completed, the students celebrated Pi Day early—with free pizza followed by apple and cherry pies baked by students in Clark’s McClaskey Culinary Institute.
Professor Tina Barsotti said, “True engineering talent emerges from embracing failure, learning from it, and using it to build something stronger, smarter, and more resilient. We must celebrate our failures as they are our connection to innovation.”
Previous engineering competition stories
Photos: Clark College/Susan Parrish and Carly Rae Zent













